Agricultural mobile machinery/vehicles are a type of machinery used in farming or other agriculture-related activities, such as harvesting. There are several types of such equipment ranging from small handhelds and power tools to tractors and large harvester to towing or operational equipment. Diverse arrays of equipment are utilized in both organic and nonorganic farming. Since the advent of mechanized agriculture, agricultural machinery has been and continues to be crucial in large-scale food production.
What’s the Agricultural Vehicles market size?
In 2019, the global agricultural machinery market was valued at USD 147 billion, with tractors being over 50% of the market share. High demand for agricultural products and increasing farm mechanization rates in developing countries have driven the growth within this industry. The Asia Pacific region is expected to grow rapidly over the forecast period due to the increase in population in countries, particularly India and China, followed by Europe and North America. China and India lead in the number of tractors sold across countries. In China, roughly 60% of all farming activities are mechanized. The farm mechanization level in India was recorded at 40%-45%, in 2017. To increase the mechanization adoption, the Indian government is promoting Balanced Farm Mechanization, by providing subsidies on various equipment and supporting bulk buying through front-end agencies, which is expected to strengthen the tractors market during the forecast period. The cost of farm labor has a direct relationship with the percentage of the total population of a country employed in agriculture, considering simple demand-supply economics, thereby, affecting the agricultural tractors market.
What are the key emerging technologies and trends in this segment?
Fig 1. Megatrends in Agricultural Vehicles Industry
Even though motorized agricultural vehicles emerged in the same generation as cars, agricultural vehicles are still primarily non-automated, non-electrified and non-digitized. This is mainly due to technological deficiencies in automation; however, this is rapidly changing. With over 100 million tons of greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union alone, the biggest culprit being Non-Road Mobile Machinery (NRMM) vehicles. Hence governments are strongly pushing for stringent regulations for pollution and noise control. Moreover, there are growing demands for operator safety and comfort along with increased productivity and efficiency due to a shortage of skilled labor. Electrification is proving to be one of the most viable strategies to meet these demands and requirements. Agricultural Tractors (ATs) is one of the key sub-segments of the NRMM witnessing the same megatrend of electrification along with precision farming and autonomous driving.
What electrification means for this segment?
Combined with precision farming and autonomous driving, the electrification yields several benefits for farmers:
- Cost savings up to 20% on seeds and fertilizers
- Cost savings on the fuel cost up to 90%
- Increased productivity resulting from constant driving and work process speed
- Savings on labor cost
- Enhanced operator safety and comfort
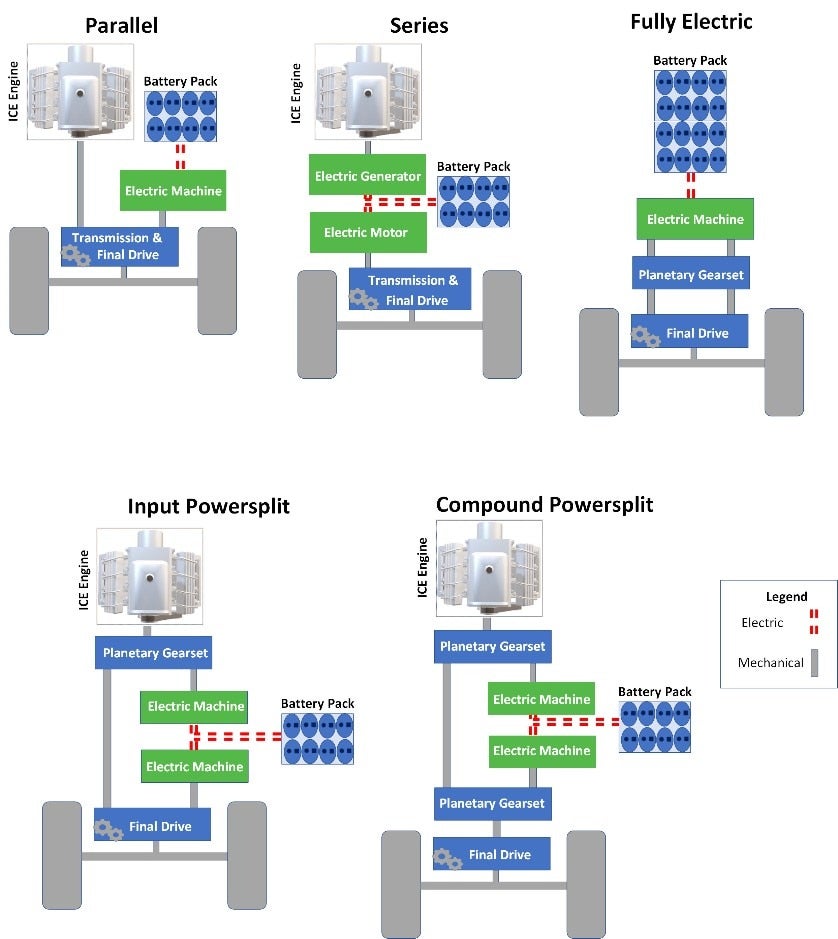
Topologies and Architecture Example
There are four main topologies for mild hybrid and hybrid electric tractor based on the power delivery configuration for propulsion and planetary gearbox, where the electric motor works along with the internal combustion engine (ICE) to improve the vehicle’s fuel efficiency, or in series with ICE to charge the battery pack. In the case of a fully battery-powered tractor, both planetary and propulsion systems are driven by electric motor either together or independently.
Fig 2. Topologies of Hybrid & Full Electric Tractor
ON Semiconductor offers a wide variety of solutions for all levels of electrification in agricultural vehicles. Solutions ranging from automotive-qualified Current Sense Amplifiers (CSA), MOSFETs and Gate Drivers for a mild hybrid 48 V architecture. The Automotive Power Module (APM) family enables 48 V and high voltage applications, e.g. 48 V BSG/ISG, motor control, 48V-12V DC-DC converter, on-board charger and HV E-Compressor for HVAC where Intelligent Power Modules (IPM) can be used, too. Also, the VE-Trac™ Dualand VE-Trac Directaddress the challenge of designing high power density scalable inverter solutions in innovative module solutions.
Let’s have a closer look at full electric battery-powered tractor topology. In this topology, the electric machine is the only source of power and it drives both the powertrain for traction and the planetary gearset for auxiliaries and hydraulic loads (either together or independently).
ON Semiconductor offers a wide variety of solutions for all levels of electrification in agricultural vehicles. Solutions ranging from automotive-qualified Current Sense Amplifiers (CSA), MOSFETs and Gate Drivers for a mild hybrid 48 V architecture. The Automotive Power Module (APM) family enables 48 V and high voltage applications, e.g. 48 V BSG/ISG, motor control, 48V-12V DC-DC converter, on-board charger and HV E-Compressor for HVAC where Intelligent Power Modules (IPM) can be used, too. Also, the VE-Trac™ Dualand VE-Trac Directaddress the challenge of designing high power density scalable inverter solutions in innovative module solutions.
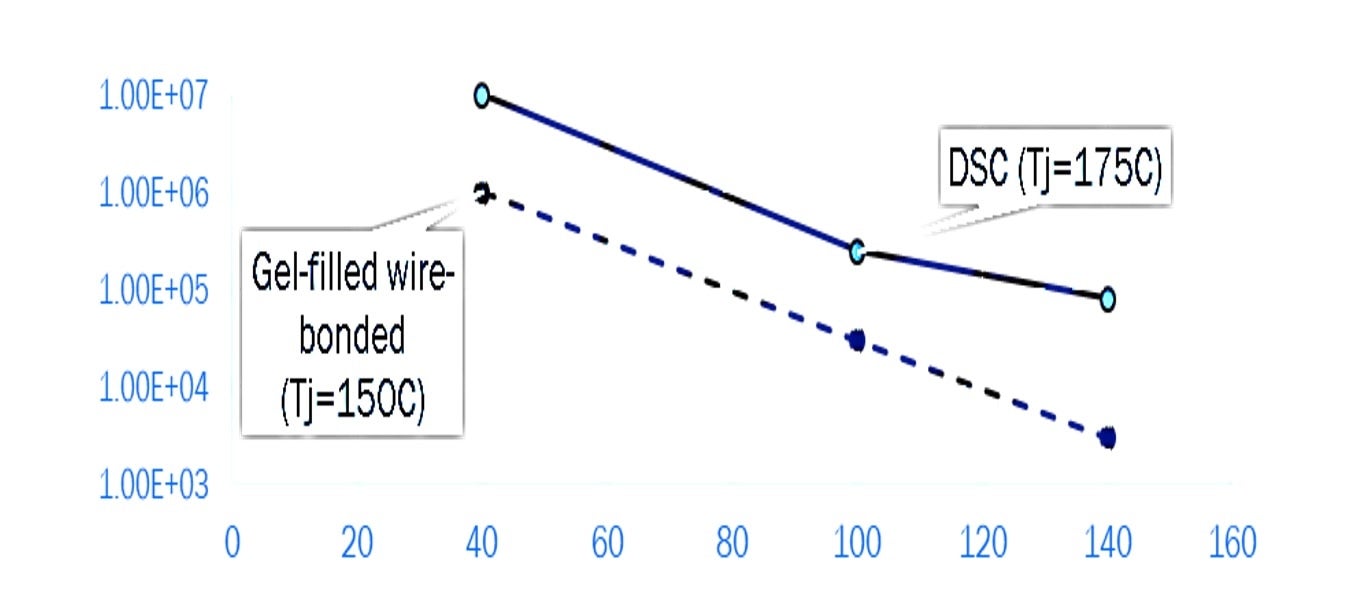
The typical power demand is in the range of 65 kW to 250 kW, quite a wide range considering the different tasks to be performed by a tractor. Considering a platform approach, scalability is a major benefit. In addition, the mission profile of a typical agricultural tractor demands high reliability, robustness and longevity without sacrificing the scalability and compact structural design. With the above considerations, the VE-Trac family of traction inverter modules from ON Semiconductor can address all the most challenging technical needs in this segment. In particular, VE-Trac Dual family represents the perfect fit for scalability, extended lifetime and reliability. All the solutions are AQG324 qualified, tested and qualified at 175oC Tj_max continuous operations, based on the mature and state-of-art FS4 750 V Narrow Mesa IGBTs technology, half-bridge (stackable) configuration in a transfer molded package. Featuring smart on-chip current and temperature sensors, performing low conduction and switching losses and extended reliability in comparison with gel-filled modules (up to 3x lifetime), the VE-Trac Dual can improve the inverter efficiency and reliability and satisfy the performance and longevity demand of Agricultural tractor mission profiles
What are the key technical challenges faced by OEMs while designing the connected and Automated vehicle (CAV)?
The key technical challenges faced by OEMs in are CAV market are:
- High energy density power source while maintaining structural integrity and size and overall system cost;
- Efficiency, because minimal downtime is crucial for the end customer to ensure low total cost of ownership;
- Longevity of the components used, as these vehicles often operate for 20 years;
- Robustness, the mission profile is mainly off-road with environment which has a higher amount of vibrations and temperature levels than the normal passenger cars.
The VE-Trac and SiC solutions from ON semiconductor check all the boxes when it comes to these requirements arising from the demanding mission profile of CAVs.
Figure 3. VE-Trac™ Dual Extended Lifetime
As part of the VE-Trac Dual, NVG800A75L4DSC can be proposed for such applications with 750V maximum voltage and 800A rated current. Moreover, ON semiconductor offers a complete ecosystem for traction inverter design with its automotive isolated high current and high-efficiency IGBT Gate Drivers with internal galvanic isolation, automotive-qualified communication, power management and signal processing and conditioning solutions.
Additionally, for quick prototyping and evaluation, the use of the NVG800A75L4DSC-EVK kit is highly recommended.
ON Semiconductor with its innovative solutions will continue to address the challenges of agricultural tractor electrification at every stage of xEV-Tractor development.
Be sure to subscribe to our blog and follow us on social media to receive the latest updates on our technologies, solutions and company news!
Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | YouTube